Wisdom teeth extraction can be a nerve-wracking experience for many individuals. After the surgery, patients face a daunting road ahead as they recover from the painful procedure. One common concern raised by many who had their wisdom teeth removed is when the stitches will disolved.
The dissolvable sutures are an essential component of the healing process as they help to close up the wound and reduce to risk of infection. These stitches typically dissolve on their own within 1 to 2 weeks after the wisdom teeth removal surgery. However, the exact time frame can. vary depending on the type of suture material used as well as the individual’s healing process.
Understanding how these sutures work and when they dissolve can help patients prepare for a smooth recovery. In the rest of this article, we will take a deep dive into how the suture works as well as offer tips on how to care for your stitches during the recovery process.
How Do Stitches Work?
Stitches are a form of medical thread or suture material designed to be sterile and non-reactive. The primary purpose of stitches is to bring the edges of a wound or incision together, allowing the body to heal more efficiently and minimizing the risk of a bacterial infection.
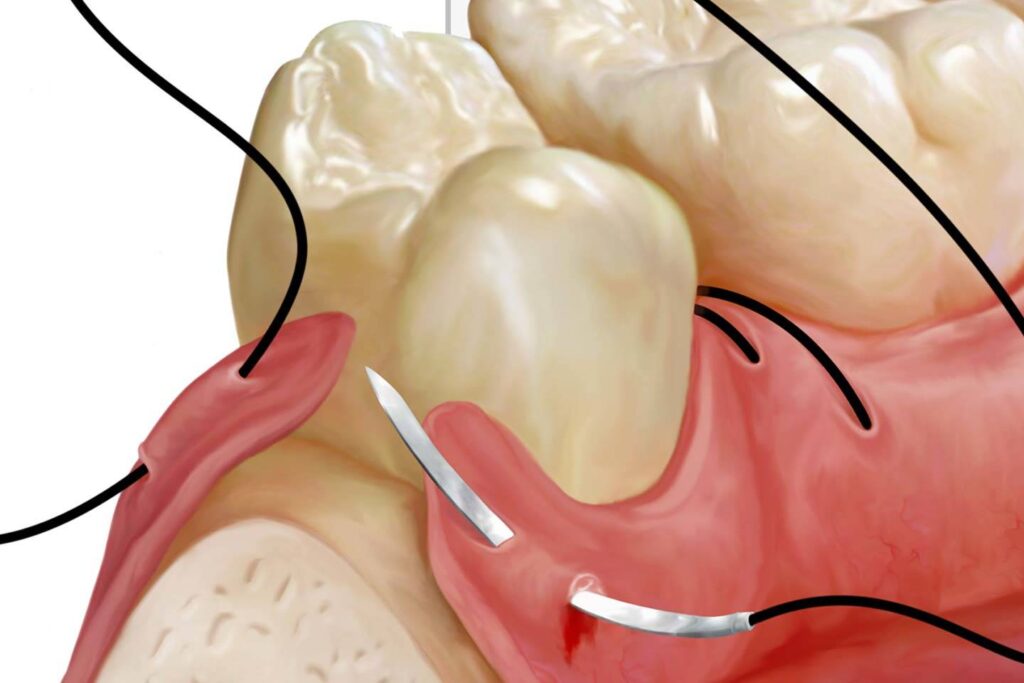
In the case of a wisdom teeth removal surgery, an incision is made on the gumline to access and remove the wisdom teeth. When a wound occurs, the body’s natural response is to start the healing process by creating a blood clot. This clot helps to stop the bleeding by creating a temporary seal over the wound. However, this blood clot is often not strong enough to hold the edges of the wound together.
With the aid of stitches, the edges of the wound can be closed up without the need for a blood clot to seal up the gap.
The stitching process typically involves using a sterile needle and thread to sew the edges of the wound together. The needle is passed through the skin on one side of the wound and then through the skin on the other side. The thread is then pulled through, bringing the edges of the wound together. Once the edges are closed, new tissue will be able to grow and eventually heal the wound.
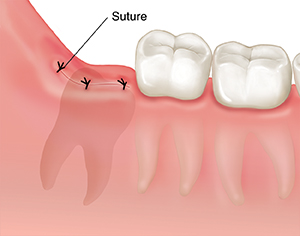
During the recovery process, the stitches will dissolve within the mouth. It takes approximately 1 week for the stitches to dissolve whereas the wound will heal completely within the first month after the surgery.
Stitches can also be divided into monofilament or braided (multifilament) suture material. A monofilament suture consists of a single strand which makes them more elastic while generating less friction when it passes through the tissue. However, it is also more slippery, making them harder to handle and secure in the wound.
On the other hand, braided suture consist of multiple strands twisted together to form a single, large strand. This makes it easier to handle and to tie secure knots, at the expense of higher fiction and increased risk of an infection.
You may be interested in: When Can I Use a Straw After Wisdom Teeth Removal and Why?
Are All Stitches Absorbable?
Not all stitches are absorbable.
For most wisdom tooth removal procedure, an absorbable stitches is used. These stitches are made of materials that break down over time within the body and do not require a follow-up appointment with the oral surgeon to remove it. Absorbable stitches are commonly used for wounds inside the body or wounds that do not require a lot of support to heal. The rate of absorption depends on the location of the wound, the type of tissue involved, and the type of suture material used. Many times, patients will feel bits of the stitches falling out from the wound; this is perfectly normal as the suture material is slowly dissolving and falling apart.
Some examples of absorbable, stitches are:
- Gut. These are made from natural materials such as cow or sheep intestines
- Polyglactin (Vicryl): This is made from a synthetic material known as polyglycolic acid.
- Polydioxanone (PDS): This is synthetic suture made from polymer of paradioxanone.
- Poliglecaprone (Monocryl): This is another synthetic suture material consisting of glycolide and caprolactone.
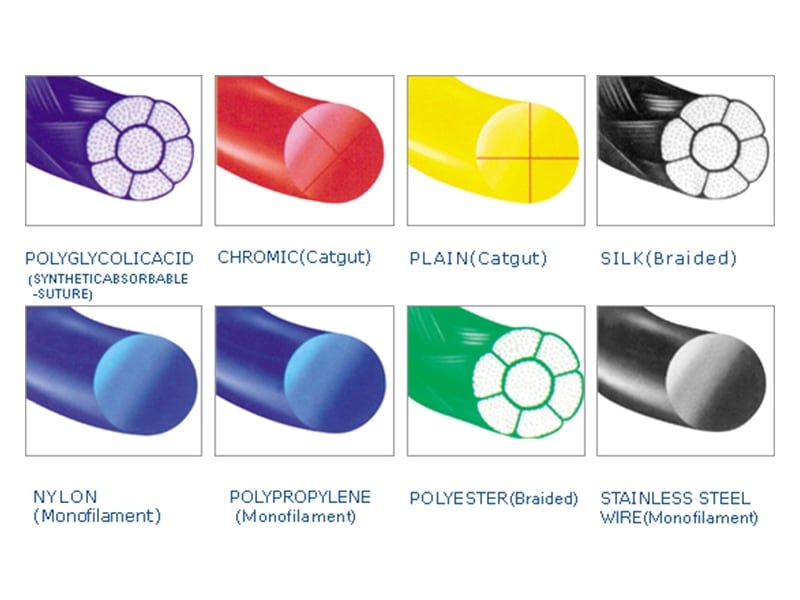
On the other hand, non-absorbable stitches are made of materials that do not break down and requires to be removed manually after the wound has healed. These stitches are used when the wound is deep or if the wound is in an area that is under a lot of tension. A non-absorbable stitches is preferred in these scenarios as it maintains significant tensile strength over an extended period of time, thus providing the much needed long-term support for the wound to heal.
Some examples of non-absorbable stitches are:
- Nylon: This is a synthetic suture made of polyamide polymer
- Silk: This is a natural suture material made from natural silk
- Polypropylene (Prolene): This is a synthetic suture material made up of an isotactic crystalline stereoisomer of polypropylene.
That said, most wisdom tooth removal surgery uses an absorbable suture material for easier post-surgery recovery.
How to Care for Stitches?
It is important that you care for your wound and stitches after the wisdom teeth removal surgery to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of infection. Here are some steps you may want to follow:
- Rinse your mouth with a saltwater mixture every day. This helps to remove any food debris that may be stuck near the extraction site and minimze the risk of an infection in the wound area.
- Avoid brushing or flossing your teeth on the extraction site for the first 72 hours. This prevents you from irritating the wound and loosening the stitches that keeps the wound closed.
- Have plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities. Sufficient rest improves the quality of your recovery. Do not take part in any physical activity or heavy lifting as you risk disrupting the recovery process and damaging the wound.
- Go on a soft food diet. Soft food such as mash potatoes, scrambled eggs, and soups reduces the risk of irritating your wound and loosening the stitches. See here for more information on the food to eat and avoid during the recovery period.
- Avoid drinking from a straw or spitting. These actions can create a suction which can disrupt the stitches and cause it to loosen. The suction force also risk causing a dry socket, a painful medical condition where the blood clot is dislodged from the wound and the nerves and bones are exposed.
Takeaway
In conclusion, the timeline for wisdom teeth stitch dissolution is typically around 1-2 weeks for absorbable sutures. During this time, it’s essential to avoid disturbing the stitches and follow your dentist or oral surgeon’s post-operative instructions carefully to promote optimal healing. While non-absorbable stitches are not typically used for wisdom teeth extractions, they may be necessary in certain cases where additional support is needed.
If the absorbable stitches are not dissolving or you are experiencing abnormal symptoms such as bad breath, bleeding, or if the pain and swelling persists unabated, contact your dentist or oral surgeon immediately as it may be signs of an infection.
By understanding the healing process and taking proactive steps to care for your stitches, you can promote a smooth and successful recovery after wisdom teeth removal.