Are you waking up with a sore jaw or experiencing tooth sensitivity you can’t explain? If the answer is yes, you may be one of the millions of people dealing with a surprisingly common yet often overlooked condition—bruxism!
Commonly known as teeth grinding, this seemingly harmless act can lead to permanent long-term effects if not diagnosed and treated early on.
In the rest of this article, we will look into bruxism and how it can affect your teeth, oral health, and overall quality of life. We will also look into the subtle signs that precede tooth wear and what you can do about it.
Whether you’re a teeth-grinder yourself, suspect you might be, or know someone who is, understanding the progression of bruxism is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. So read on to find out more about bruxism!
Understanding Bruxism
Bruxism is a medical condition characterized by the involuntary clenching or grinding of teeth, often occurring during sleep, but also potentially manifesting while awake. The act itself may seem harmless, but its recurrent nature can lead to a plethora of dental and systemic issues.
There are primarily two forms of bruxism: Sleep Bruxism and Awake Bruxism
Sleep Bruxism
This form of teeth grinding occurs during sleep cycles and is often related to other sleep disorders like sleep apnea. Individuals with sleep bruxism are usually unaware of their condition until symptoms become noticeable or a partner points it out due to the noise created by grinding.
Awake Bruxism
This happens during waking hours and is frequently associated with emotional states like stress, anxiety, or concentration. Unlike its nocturnal counterpart, awake bruxism is usually conscious, albeit involuntary, and may involve clenching rather than grinding.
Causes of Bruxism
There are a myriad causes of bruxism, encompassing a range of psychological, physiological, and lifestyle-related factors.
1. Psychological Factors
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress is often cited as a leading cause. High stress levels can lead to increased muscle tension, which in turn may lead to teeth grinding.
- Mental Health Conditions: Other mental health issues like depression can also be linked to bruxism
2. Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: High consumption of caffeine or alcohol can exacerbate symptoms.
- Chewing Habits: People who habitually chew on pens, pencils, or other objects may be more prone to bruxism.
3. Physiological Factors
- Misaligned Teeth or Abnormal Bite: Dental issues can sometimes cause or exacerbate teeth grinding. If teeth don’t align properly, the jaw muscles may work overtime, leading to grinding.
- Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMJ): Existing TMJ disorders can worsen bruxism or vice versa.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and parasomnias are often associated with sleep bruxism.
- Neurological Conditions: In some cases, conditions like Parkinson’s disease can contribute to bruxism.
You may be interested in: Will Listerine Kill Tooth Infection?
4. Pharmacological Influences
- Medications: Certain types of medications, particularly antidepressants and antipsychotics, have been linked to bruxism.
- Substance Use: Stimulants like caffeine, alcohol, and recreational drugs can increase the likelihood of grinding teeth.
Interestingly, genetic predispositions may also play a role in bruxism. While the link isn’t definitively proven, a family history of the condition suggests a possible genetic component.
As seen, bruxism is a complex condition that can be the result of multiple contributing factors that spans across psychological, physiological, pharmacological, and potentially even genetic domains. So what does teeth grinding look like before and after?
Before and After of Teeth Grinding
The before and after stages of teeth grinding due to bruxism are distinct, with differing symptoms, consequences, and treatment requirements.
In the early stages of bruxism, you might experience minor tooth sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods or feel a slight discomfort in your jaw. At this point, the condition might only be detectable through professional dental check-ups, which can reveal early signs of enamel wear.
As bruxism progresses to the intermediate stage, symptoms become more pronounced. The occasional jaw discomfort may evolve into frequent tension headaches or even migraines. There may be increased sensitivity in the teeth, and dental check-ups might reveal more significant enamel wear. At this point, your dentist may will recommend treatments such as specialised mouthguard, medications for pain relief, or even cognitive behavioral therapy if it is attributed to stress or anxiety.
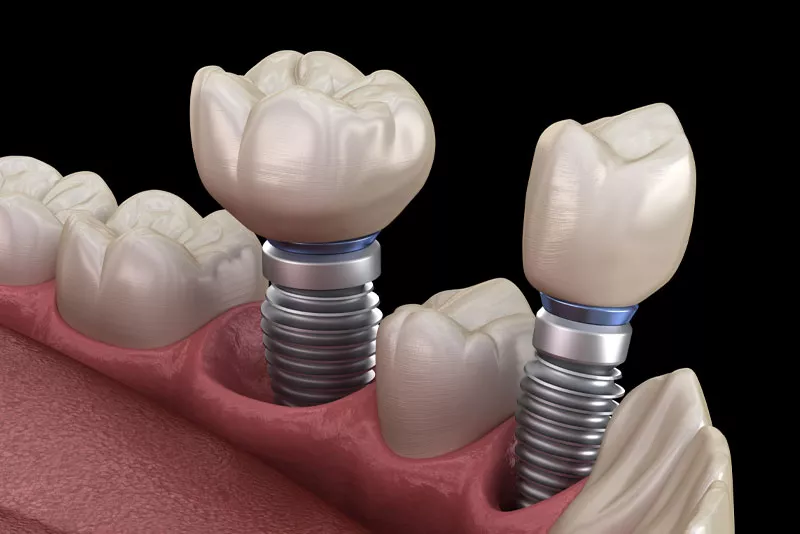
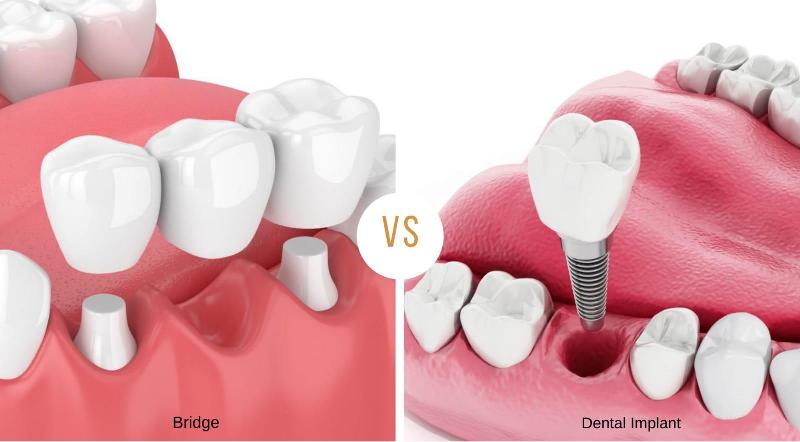
If left untreated, bruxism can cause severe symptoms at the advanced stage. Constant grinding can result in flattened, fractured, or even loose teeth. Chronic jaw pain and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders often become a significant concern. In most cases, it will lead to a host of other dental problems including gum recession and bone loss in the jaw. A multi-pronged treatment will be necessary at this point in time. Restorative treatment such as dental implants or dental bridges may be needed in order to replace any loose tooth.
Looking to make your own mouthguard? Read: How to DIY Your Homemade Mouth Guard for Sleeping
Closing Thoughts
In wrapping up our exploration of the effects of bruxism, it’s clear that this condition is not just a simple habit of teeth grinding, but rather a complex issue that requires multi-faceted understanding and intervention.
We’ve discussed how bruxism can stem from various factors—be it psychological stress, dental misalignments, or even genetic predisposition. Furthermore, the symptoms grow in severity if not addressed timely, making early detection crucial.
From the early stage, where symptoms are mild and often overlooked, to the advanced stage, where severe dental damage and chronic pain become real challenges, bruxism evolves in a way that can significantly impact quality of life.
If you’re grinding your way through life, understand that solutions exist at every stage. The first step is awareness, and from there, a tailored, comprehensive treatment plan can guide you back to dental health and overall well-being.